Functions of the Human body
The difference between Anatomy and Physiology
This knowledge will enable you to provide effective health care with all information related to human body organs and functions, you really need to familiarize yourself with normal anatomy or a structure and physiology or functioning of the human body.
Anatomy
The branch of science that deals with the structure of the human body parts and their forms and arrangements.
Physiology
This is concerned with the functions of the body parts , what they do and how they do it

The body’s function are conducted by Organs
The different body systems
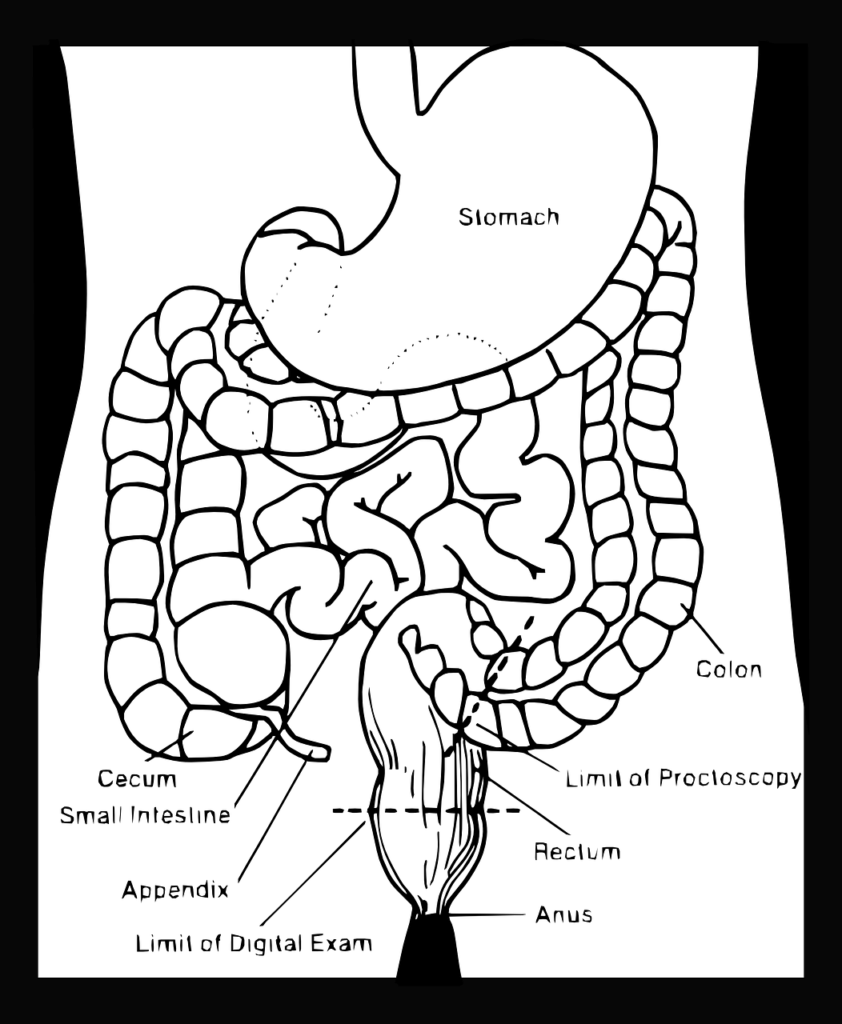
Human Digestive systems
Organs and functions
Mouth: Receive food ,chew the food
Liver: Oxidation of fatty acids and Protein and carbohydrates metabolism
Large intestines: Forces out form the body
Small intestines: Secretes hormones and digestive enzymes
Stomach:Degests food
Human urinary system and function
Kidney :They remove metabolic wastes from the blood and excrete them to the outside
Ureter: Conveys urine from the kidney to the bladder
Urinary bladder: Stores urine
Urethra: Conveys urine from the bladder and outside the body
Human lymphatic system
Human lymphatic system
The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system.
Immunity: The body’s defense mechanisms against organisms such as fungi , bacteria and viruses
Spleen: It acts as a blood reservoir ; filters foreign particles and damaged blood cells from the blood
Lymph nodes: They are the centers of production of lymphocytes which fights infections.
human respiratory system and their function
Nose :Smell and warms and moisturizes air
Lungs: contains air passages , blood vessels
Pharynx: Air distribution passages
Larynx: Houses the vocal cords
Trachea: Leads the larynx to the bronchi
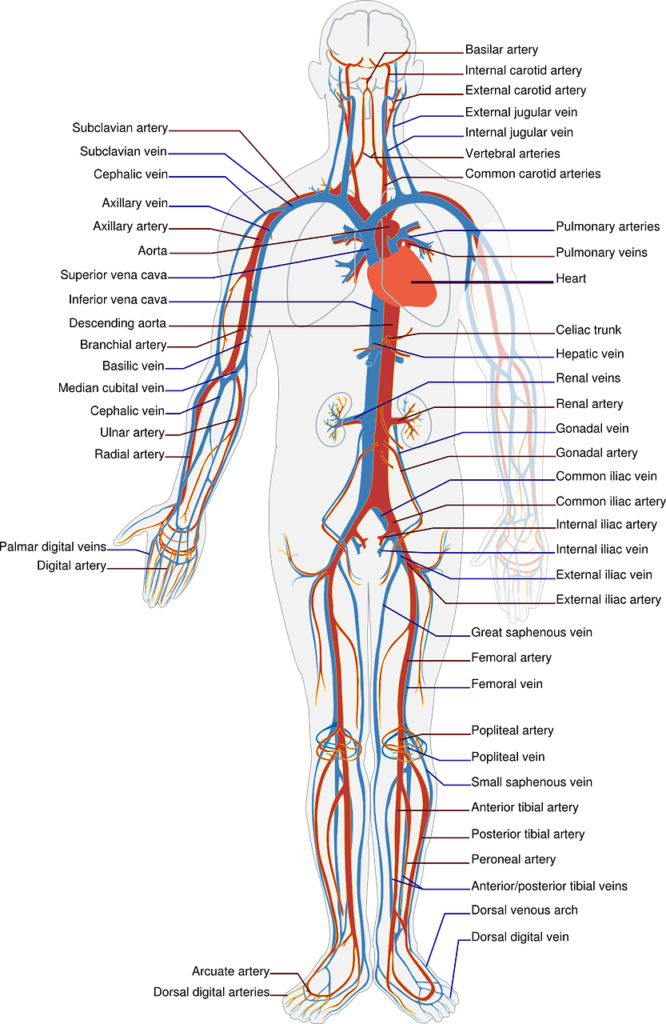
Human cardiovascular system
Heart :Distributes blood to the whole body
Blood vessels :Carries the blood throughout the body ,
Veins– carry the blood to the heart to be oxygenated
Human muscular system
Muscles:[smooth , skeletal and cardiac] Skeletal muscles contraction and relaxation of muscles e, g running , walking all body movements and muscles fatigue is when a muscle loses it’s ability to contact.
Human male reproductive system
Bladder: Hold urine
Penis :Conveys urine and seminal fluid and sex organ
Anus: To defecate
Glans penis: The cone shaped part of the penis
Scrotum :Provides a covering for testes
Urethra :Conveys urine from bladder to outside body
Testes :Primary sex organ and sperm cells reformed, male sex hormones are formed
Human female reproductive system
Anus :To defecate
Cervix :Neck of the uterus
Vagina :Receive penis during sex
Urethra :Conveys urine from the bladder
Ovary :Produce female sex egg cells
Uterus :Receives fertilized egg
Uterine :Convey egg cells to uterus
The skin and the integumentary system
Epidermis: It is a protective covering for the body , also protects underlying tissues against water loss , mechanical injury and the effects of harmful chemical and also get ride of waste ,those are aids in the regulation of body temperature.
The Epidermis is the outer layer of skin composed of stratified squamous epithelium which lacks blood vessels , and the thickness of the epidermis varies in different types of skins. It is the thinnest on the eyelids at 0.5 mm and the thickest on the palms and soles at 1.5mm.
types of bones
Long bones
Short bones
Flat bones
Long bones :They have the longitudinal axes and expanded ends e, g arms and legs
Short Bones :They are cube like and their lengths and width are roughly equal e, g wrists and ankles
Flat bones :They are plate like structures with broad surfaces e ,g the ribs ,scapulae , bones of the skull.
Bones
Skull :Houses the brain and facial bones
Upper limb-arms :Carry ,hold hands
Hand :Touch all activities of daily life
lower Limb -legs and feet :stand and walk

